Prospect Theory: Understanding Risk and Ambiguity in Decision-Making

Prospect theory is a behavioral economics theory that describes how individuals make decisions under risk and ambiguity. It was developed by Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky in 1979 and has since become one of the most influential theories in behavioral economics.
Prospect theory challenges the traditional economic model of rational choice, which assumes that individuals are rational actors who make decisions based on objective probabilities and expected utility. In contrast, prospect theory suggests that individuals are often irrational and make decisions based on heuristics and biases.
4.6 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 16822 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 517 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Key Features of Prospect Theory
Prospect theory is characterized by several key features:
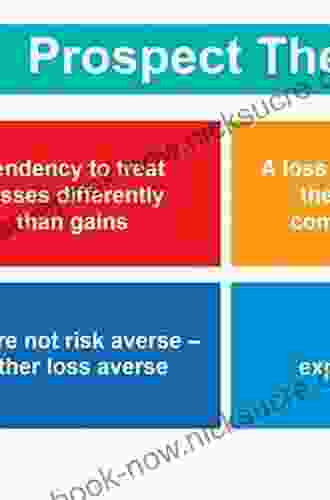
1. Reference Point: Individuals evaluate gains and losses relative to a reference point, which is typically the status quo. Gains are perceived as positive deviations from the reference point, while losses are perceived as negative deviations.
2. Loss Aversion: Individuals are more sensitive to losses than gains, meaning they place a greater weight on potential losses when making decisions. This asymmetry in perception can lead to risk-averse behavior in situations involving potential losses.
3. Diminishing Sensitivity: The sensitivity to gains and losses decreases as the magnitude of the deviations from the reference point increases. This means that individuals become less sensitive to extreme gains and losses as they become larger.
4. Curvature of the Value Function: The value function, which represents the utility of gains and losses, is concave for gains and convex for losses. This curvature reflects the fact that individuals experience diminishing sensitivity as the magnitude of the deviations from the reference point increases.
Implications of Prospect Theory for Risk-Taking
Prospect theory has significant implications for understanding how individuals make decisions under risk. It suggests that:
1. Risk-Averse Behavior: Individuals tend to be risk-averse when faced with potential losses, meaning they prefer to avoid risks that could lead to negative deviations from the reference point.
2. Risk-Seeking Behavior: Individuals may exhibit risk-seeking behavior when faced with potential gains, meaning they may be willing to take risks that could lead to positive deviations from the reference point.
3. Endowment Effect: Individuals place a higher value on goods that they already own, which can lead to a reluctance to sell or trade these goods.
4. Framing Effects: The way a decision is presented can influence an individual's perception of risk and their willingness to take risks.
Extensions of Prospect Theory
Since its initial development, prospect theory has been extended to account for additional factors that influence decision-making:
1. Time Sensitivity: The perceived value of gains and losses can differ depending on the time horizon over which they are realized.
2. Social Comparison: Individuals' decisions can be influenced by comparisons with others, particularly in situations involving social norms and fairness.
3. Emotional Factors: Emotions, such as fear and regret, can play a role in decision-making, particularly in situations involving high stakes or uncertain outcomes.
Applications of Prospect Theory
Prospect theory has been applied in various fields, including:
1. Finance: Prospect theory helps explain why investors may be more likely to hold onto losing investments due to loss aversion and the endowment effect.
2. Marketing: Marketers can use prospect theory principles to design promotions and products that appeal to consumers' risk preferences and loss aversion.
3. Public Policy: Governments can use prospect theory to design policies that encourage positive behaviors and discourage negative behaviors by framing decisions in a way that aligns with individuals' risk preferences.
4. Health: Prospect theory can help explain why individuals may be more likely to engage in risky health behaviors despite knowing the potential negative consequences.
Prospect theory is a powerful behavioral economics theory that provides insights into how individuals make decisions under risk and ambiguity. It has challenged the traditional economic model of rational choice and has implications for a wide range of fields, including finance, marketing, public policy, and health.
By understanding the key features and implications of prospect theory, individuals and organizations can make more informed decisions and design policies and strategies that better align with human behavior.
4.6 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 16822 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 517 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Best Book Source
Best Book Source Ebook Universe
Ebook Universe Read Ebook Now
Read Ebook Now Digital Book Hub
Digital Book Hub Ebooks Online Stores
Ebooks Online Stores Fiction
Fiction Non Fiction
Non Fiction Romance
Romance Mystery
Mystery Thriller
Thriller SciFi
SciFi Fantasy
Fantasy Horror
Horror Biography
Biography Selfhelp
Selfhelp Business
Business History
History Classics
Classics Poetry
Poetry Childrens
Childrens Young Adult
Young Adult Educational
Educational Cooking
Cooking Travel
Travel Lifestyle
Lifestyle Spirituality
Spirituality Health
Health Fitness
Fitness Technology
Technology Science
Science Arts
Arts Crafts
Crafts DIY
DIY Gardening
Gardening Petcare
Petcare Carlos G Groppa
Carlos G Groppa Neil Ansell
Neil Ansell Norman Cooley
Norman Cooley Pocahontas Gertler
Pocahontas Gertler Cheryl Pallant
Cheryl Pallant Arabella R Irvine
Arabella R Irvine Anita Anand
Anita Anand Norman Gelb
Norman Gelb Jean Edward Smith
Jean Edward Smith Anne Case
Anne Case David Barnett
David Barnett Val Breit
Val Breit Abdel Bari Atwan
Abdel Bari Atwan Michael Mcgaulley
Michael Mcgaulley Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie Daniel Macmillan
Daniel Macmillan Patrick Farenga
Patrick Farenga Chris Hedges
Chris Hedges Ruth Bader Ginsburg
Ruth Bader Ginsburg Ana Alejandra Germani
Ana Alejandra Germani
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Garrett BellMastermind of Dunkirk and D-Day: The Extraordinary Life and Legacy of Bernard...
Garrett BellMastermind of Dunkirk and D-Day: The Extraordinary Life and Legacy of Bernard... Juan ButlerLamy Of Santa Fe Paul Horgan: The Enchanting Realm of a Literary Icon in the...
Juan ButlerLamy Of Santa Fe Paul Horgan: The Enchanting Realm of a Literary Icon in the... Jett PowellFollow ·2.7k
Jett PowellFollow ·2.7k Calvin FisherFollow ·15.9k
Calvin FisherFollow ·15.9k Don ColemanFollow ·17.1k
Don ColemanFollow ·17.1k Herman MitchellFollow ·19k
Herman MitchellFollow ·19k Jaden CoxFollow ·11.9k
Jaden CoxFollow ·11.9k Nikolai GogolFollow ·9.4k
Nikolai GogolFollow ·9.4k Jorge AmadoFollow ·15.8k
Jorge AmadoFollow ·15.8k Vincent MitchellFollow ·12.4k
Vincent MitchellFollow ·12.4k

 Asher Bell
Asher BellChris Hogan: The Everyday Millionaire Who Shares His...
Chris Hogan is an Everyday Millionaire who...

 Robert Browning
Robert BrowningThe Comprehensive Guide to Compensation, Benefits &...
In today's...

 Allen Parker
Allen ParkerApproving 55 Housing Facts That Matter
Housing, an essential aspect...

 J.D. Salinger
J.D. SalingerUnveiling the Enchanting Heritage of Royal Tours: A...
Canada, a land steeped in history...
4.6 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 16822 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 517 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |